Hip Osteoarthritis
Posted on 03rd May 2017 / Published in: Hip

Hip osteoarthritis literally means wear and tear to the hip joint, or hip joint degeneration. Similar to other joints carrying your weight, the hips are prone to wear-and-tear arthritis. The glistening and smooth cartilage at the end of the bones that allows the hip joints to glide smoothly may end up wearing thin.
The first sign of osteoarthritis might be a small amount of discomfort and stiffness in the thigh, buttock or groin upon waking up in the morning. Pain flares up when you are more active and tends to get better upon resting. If you don’t get treatment for the condition, it will keep getting progressively worse until resting isn’t able to relieve your pain any longer. The joint will get inflamed and stiff. Bone spurs can build up at the joint edge.
You might also notice some pain travelling down the front of the thigh to the knee, and this is referred pain from the hip. You will also notice you are having difficulty getting your socks on in the morning as you gradually lose the ability to bend the hip.
When the cartilage is completely worn away, the bones end up rubbing against one another, and the body lays down bone around the joint which makes it difficult to move. You can lose the ability to flex, rotate or extend your hip. If you are less active in an attempt to avoid the pain, the muscles that control the joints become weak and you might start limping.
Hip arthritis sufferers will notice that their hip pain can flare up, or reduce in nature over any particular week. This is due to inflammation. If you have any pain in the groin or hip, make sure you see your therapist as soon as possible because treatment to the hip can be very beneficial and reduce the onset of arthritis.
Hip Osteoarthritis Anatomy
The hip joint, like the shoulder joint, is a ball and socket joint. It’s designed for mobility and stability, so it has a deep socket.
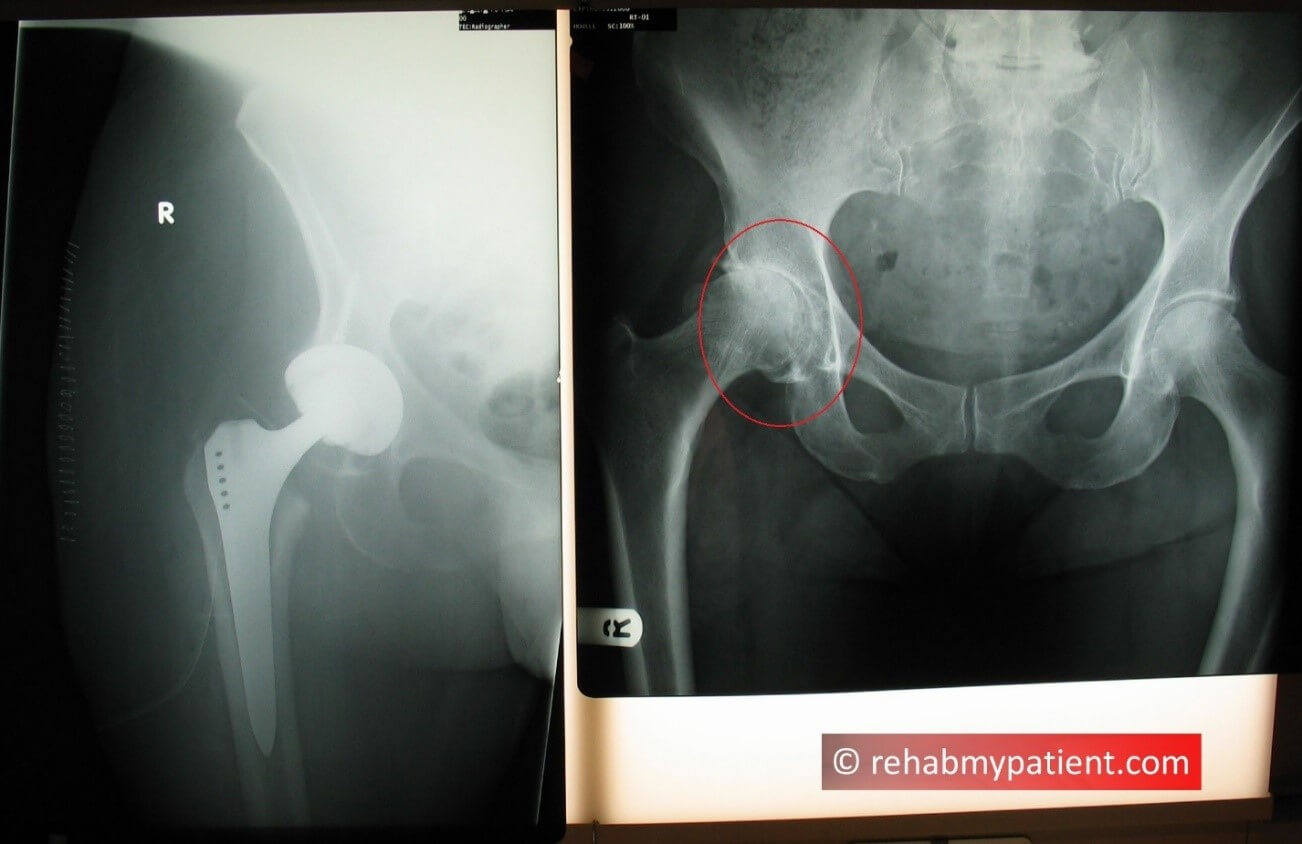
Hip osteoarthritis on the right hip and hip replacement
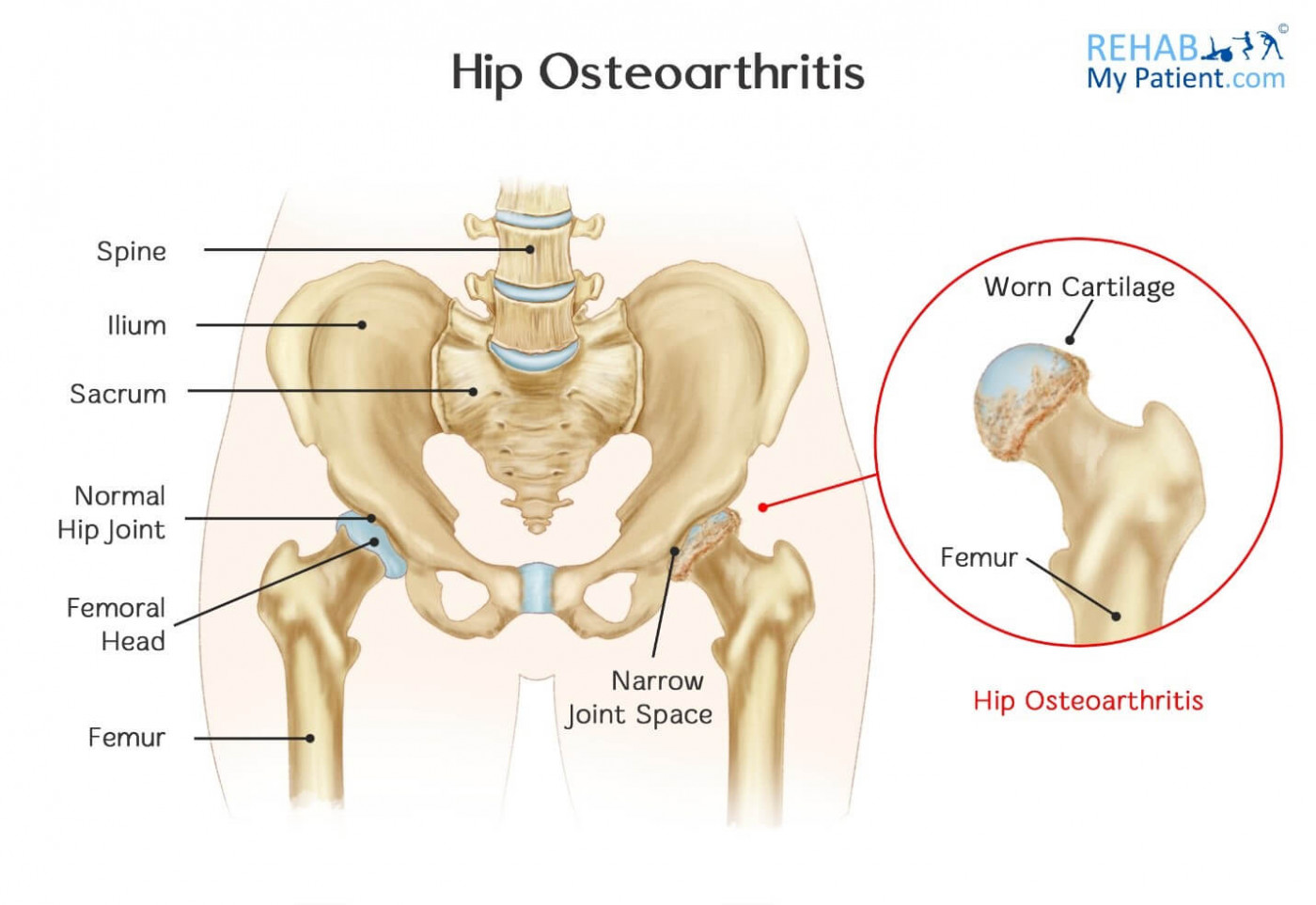
This allows good movement but helps to keep the joint secure. There are plenty of ligaments and muscles around the hip. The main muscles are the gluteal muscles (buttock muscles), the adductors (groin muscles), the quadriceps (front thigh muscles) and the hamstrings (back thigh muscles). The main bone in the hip is the femur, and the ball at the end of the femur is called the femoral head. There is a femoral neck just before the femoral head. The socket is called the acetabulum and is part of the pelvis.
It is worth noting the difference between osteoarthritis of the hip and osteoporosis of the hip. The former is degenerative change or wear and tear. The latter is where the hip joint suffers from bone thinning. Osteoporosis leaves patients vulnerable to fracture if they fall.
How to Treat Hip Osteoarthritis:
- Gentle Mobility
The big question is, should you rest or do exercise? The answer is: exercise – but gently. It’s good to keep mobile so things like walking, swimming and water aerobics are excellent exercises. You can also cycle, row, and go on the cross-trainer. But respect your body’s limitations, start slowly, and build up your fitness carefully. Stop if you get any pain or problems and go back to your therapist.
- Physical Therapy
Make sure you get a course of treatment from your therapist. They will improve range of mobility at your hip joint, reduce inflammation, give you advice about sleeping, moving, and using ice/heat, and also give you strengthening exercises.
- Reduce Inflammation
An anti-inflammatory medication is not only good for minimizing the swelling, but it is also good for helping to combat pain. But it is not a long term solution, so far better is ice/heat which is a technique called contrast bathing. It helps to reduce inflammation and swelling. Discuss this technique with your therapist and opinions differ on how long to use the ice and heat for.
- Sleep
Make sure your body is getting an adequate amount of sleep every night. Your body needs time to heal and recover fully between any activities so as to avoid undue stress.
- Lose Weight
If you are currently overweight, you need to lose any excess weight to reach an ideal weight. As the disease progresses further, you will find that you have to use a cane to get around.
- Walking Stick
Use a crutch or walking stick if your mobility gets too bad, it will help to offload strain on the hip.
Tips:
- Roughly 10 million Americans have been diagnosed with osteoarthritis.
- If you have a family history of the disease, you are at an increased chance of getting the disease.
- For those who are obese, elderly or have injuries placing stress on the hip cartilage, you are at an increased risk for osteoarthritis.
- Even if you have no other risk factors, you can still develop the condition.
- If you think you may have the condition, make sure to speak with your provider right away.
Sign UP
Sign up for your free trial now!
Get started with Rehab My Patient today and revolutionize your exercise prescription process for effective rehabilitation.
Start Your 14-Day Free Trial