Mid Scalene
Posted on 27th Jul 2020 / Published in: Neck

General information
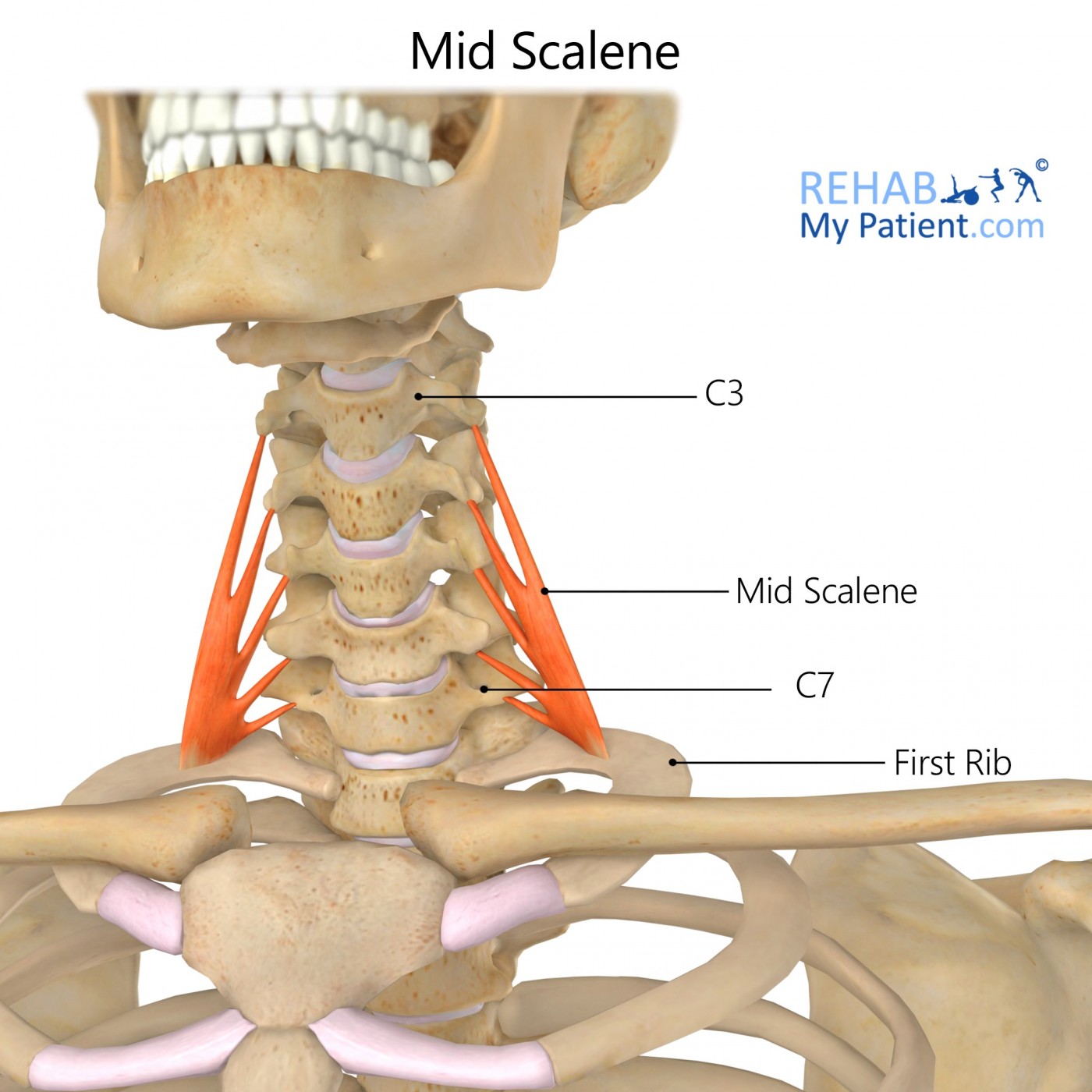
The mid scalene descends upon the vertebral column and is an accessory muscle for respiration.
Literal meaning
The middle muscle of the group of muscles making up a triangle shape.
Interesting information
The mid scalene, or middle scalene, is a skeletal muscle of the neck that is responsible for rotating the neck from side to side and elevating the first rib.
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (TOS) is a rare condition that affects the mid scalene and other muscles of the neck by the exertion of pressure on the nerves and blood vessels in the surrounding area. Injury can occur through trauma, repetitive activities, pregnancy, poor posture, or anatomical defects. Neurological TOS is the most common form and includes symptoms of tingling and numbness in the fingers, pain in the shoulder or neck, and a weakened grip. Due to the risks involved when performing surgery to treat this, doctors and chiropractors often prefer the conservative approach when treating this condition. If left untreated, permanent nerve damage may occur. Three forms of treatment in combination with each other often yield successful results in aiding with TOS. Relaxation techniques help to relieve the tension in the neck and shoulder area, helping to reduce compression of the nerves and blood vessels. Physical therapy exercises strengthen muscles and retrain them to take pressure off the blood vessels. Muscle relaxants or pain medication can reduce muscle inflammation, which helps muscles to relax.
Origin
Posterior tubercle of the transverse processes of the lower six cervical vertebrae C2-7.
Insertion
Upper surface of the first rib.
Function
Elevation of the first rib.
Rotation of the neck to the opposite side.
Nerve supply
Ventral rami of the third to the eighth cervical spinal nerves.
Blood supply
Ascending cervical artery.
Relevant research
Case studies reveal that chiropractors and doctors should be aware of anatomical anomalies occurring that may make a patient more susceptible to Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (TOS). A case study shows that upon dissection of a male cadaver, students discovered the bifurcation of the anterior scalene, splitting the muscle into a posterior and an anterior section surrounding the right subclavian artery. Abnormally running between the posterior section of the anterior scalene and the mid scalene were the trunks of the brachial plexus. Due to the odd locations of the artery and the brachial plexus, complications could arise due to compression and TOS could occur.
Goubran, E, Carlos, J, Samir, A. (2010). “A bifurcated anterior scalene muscle: A case report”. Clinical Chiropractic. 13:2, 153-155.
Mid scalene exercises
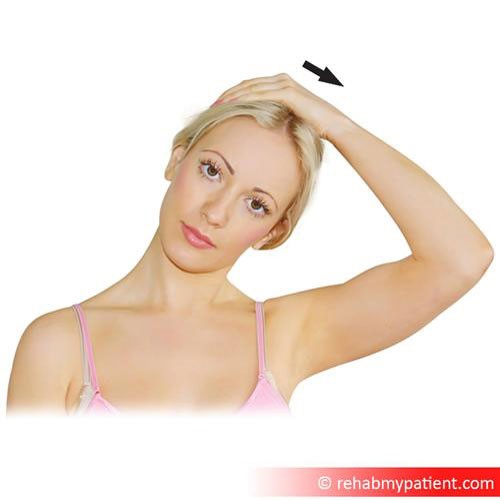

Neck stretch for Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
To begin the stretch, place the affected arm behind the head, using the affected hand to hold the head steady. Turn head slowly away from pain only until feeling a slight stretch, hold in place for thirty seconds. Return to normal position, rest for ten seconds, and repeat. Perform five repetitions of this exercise a day to help with TOS.
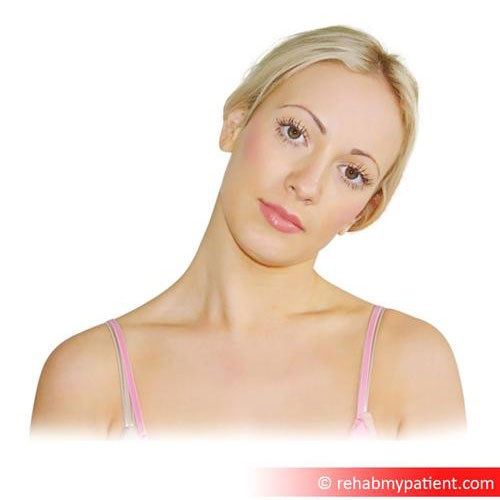

Scalene stretch
Making sure to keep both shoulders down, bend head to either side, bringing the ear towards the shoulder, and hold for thirty seconds. Resume starting position and repeat on the other side. Perform this stretch three times a day.
Sign UP
Sign up for your free trial now!
Get started with Rehab My Patient today and revolutionize your exercise prescription process for effective rehabilitation.
Start Your 14-Day Free Trial