Calcific Tendinopathy of the Shoulder
Posted on 09th Sep 2017 / Published in: Shoulder

An individual suffering with tendinopathy will have inflammation of the surrounding shoulder joint tendons. Four muscles and tendons are in the rotator cuff, which surrounds the back and top of the shoulder. The tendons work together to hold the scapula and humerus together, as well as aid in shoulder movement. Calcific tendinopathy is also known as calcific tendonitis, and may be related or referred to as shoulder impingement.
The first process that occurs is inflammation of the rotator cuff tendon. Typically this tendon is the supraspinatus tendon, and inflammation can occur gradually due to poor posture, arthritis, or a small bone abnormality at a small joint in the shoulder called the AC joint. When the tendinopathy progresses, the body lays down calcium deposits in the tendon to harden and protect the tendon from the inflammation or rubbing of the bone on it. Hence the term, calcific tendinopathy.
Calcific Tendinopathy of the Shoulder Anatomy
The rotator cuff is a main component of the shoulder joint. The joint provides motion between the scapula and the humerus. The shoulder joint itself is a ball and socket. Depressing the scapula provides a socket for the humerus head. Muscles and ligaments work to stabilize the joint throughout use. 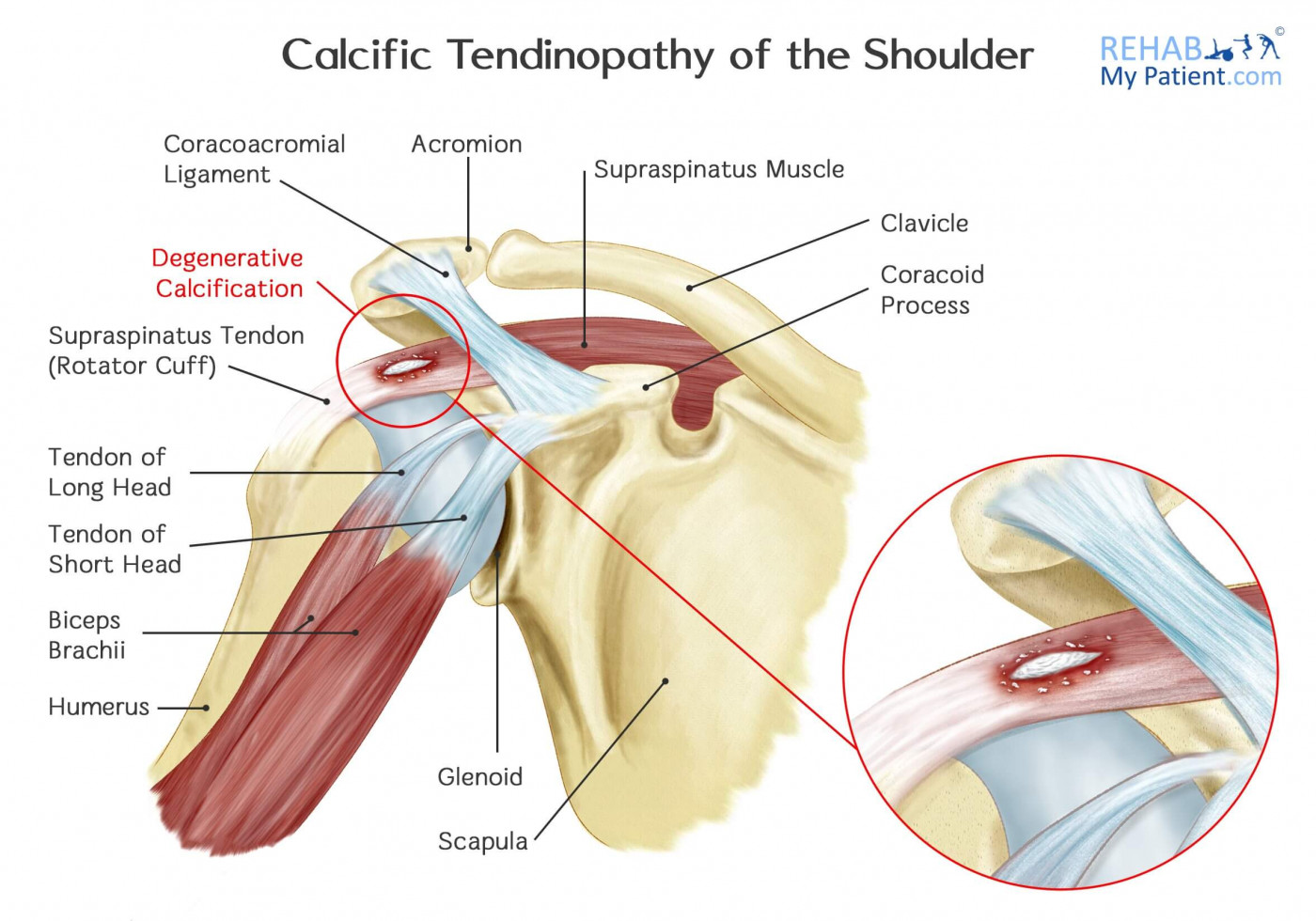
In the pre-calcific stage, tendons change in ways that make the deposits more likely to form. During the calcific stage, the crystals are deposited into the tendons where they begin to disappear. The body ends up reabsorbing the calcium deposits. When the body reabsorbs the deposits, the most pain will occur. In the post-calcific stage, the body works to heal the tendon before being remodeled with new tissue. Once the process occurs, the pain will diminish or go away completely.
How to Treat Calcific Tendinopathy of the Shoulder:
- Manual Therapy
Manual or physical therapy is very good at treating calcific tendinopathy. Your therapist will work to reduce inflammation in your shoulder, thereby reducing the further buildup of calcium deposits. Soft tissue tightness, postural problems, and instability in the shoulder can also be addressed through treatment and exercise prescription. Ultrasound, acupuncture, ice therapy and LASER can also help.
- Anti-Inflammatory Medications
The first goal is to control inflammation and pain. Resting and taking an anti-inflammatory medication will help to control your pain. By relieving some of the swelling and making you comfortable, the process of healing is simpler. Use for short periods of time only.
- Cortisone Injection
If the pain is still severe after other treatments, cortisone injections are a powerful steroid that might work to alleviate the pain and pressure. Cortisone works to temporarily ease swelling and inflammation.
- Saline
During the time when the deposits are reabsorbed, the pain can become quite excruciating. Removing the calcium deposit through an insertion of two large needles into the affected area and rinsing with a saline solution might prove beneficial. The procedure can break the calcium particles free, which allows them to be removed with the needles. Eliminating the calcium deposits will aid in the healing process. Even if the procedure doesn’t remove all of the deposits, it can help to reduce the pressure within the tendon to help alleviate pain.
Tips:
- Avoid lifting heavy objects to prevent placing undue strain on the shoulder joint.
- Prolonged, repetitive activities such as painting, construction or sports, can cause the shoulder to become inflamed and swollen.
- Elderly individuals are more prone to calcium deposits, so extra care and precaution needs to be taken.
- Those suffering with osteoarthritis are more susceptible to the development of the deposits.
- When participating in sports, make sure to pay attention to any pain and inflammation in the shoulders as that could be a sign of something more severe.
- Keep good posture which will place the shoulders in a correct anatomical position, reducing strain on the rotator cuff tendons.
Sign UP
Sign up for your free trial now!
Get started with Rehab My Patient today and revolutionize your exercise prescription process for effective rehabilitation.
Start Your 14-Day Free Trial