Tranversus Abdominis
Posted on 30th Jul 2020 / Published in: Abdomen

General information
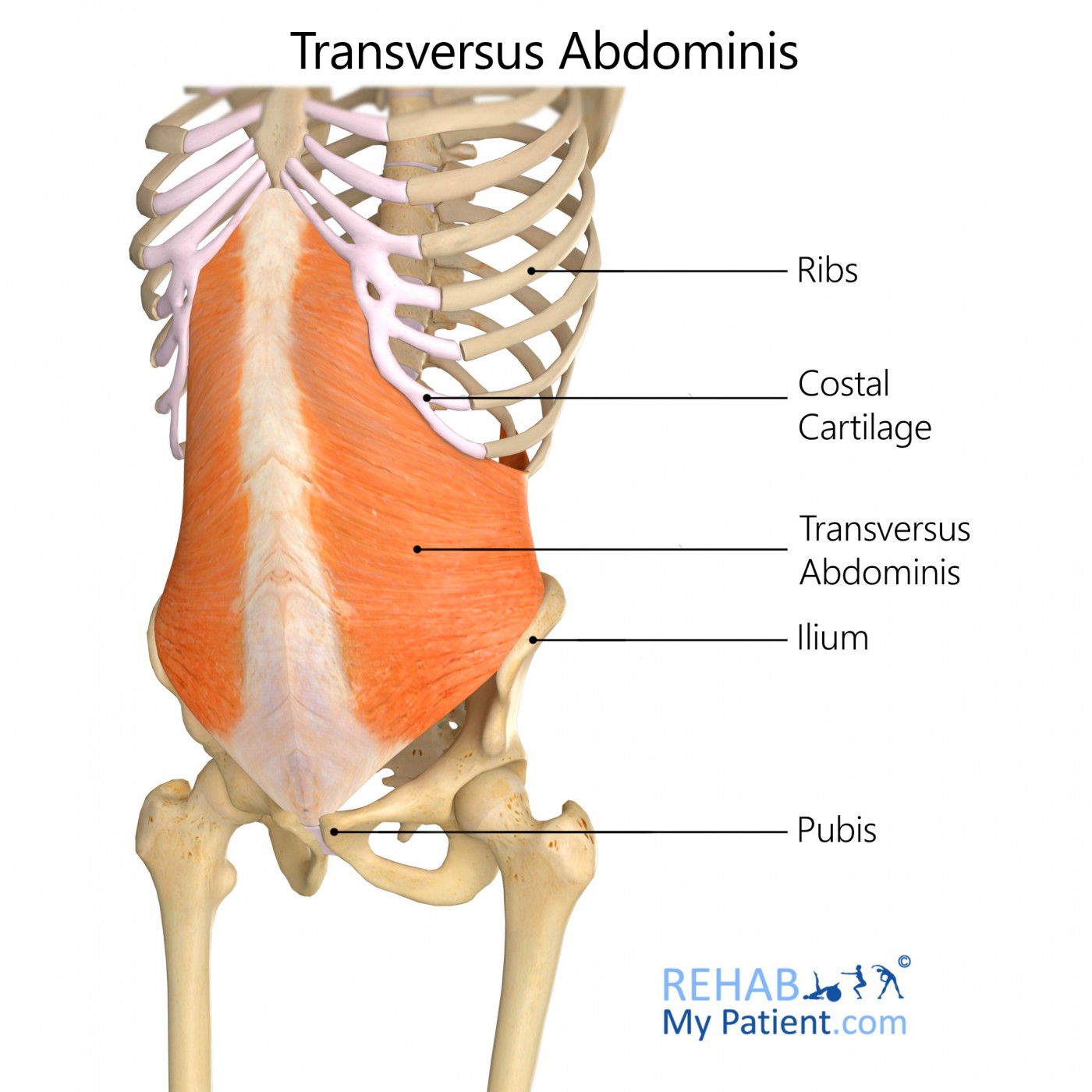
The transversus abdominis is a broad muscular sheet situated on both the lateral sides of the abdominal wall. This muscle, along with the external abdominal oblique and the internal abdominal oblique, make up the lateral abdominal muscles. Further, this muscle comprises the anterolateral abdominal wall, along with the rectus abdominis and pyramidalis.
Literal meaning
The crosswise muscle of the belly.
Interesting information
This muscle fibres’ have a transverse orientation and sit perpendicular to the linea alba. In order to maintain normal abdominal tension this muscle works the other abdominal muscles as well as playing an important role in increasing intra-abdominal pressure.
Origin
Internal surfaces of costal cartilages of ribs 7-12, thoracolumbar fascia, anterior two thirds of iliac crest, iliopectineal arch.
Insertion
Linea alba, aponeurosis of internal abdominal oblique muscle; pubic crest, pectineal line of pubis.
Function
Bilateral contraction - Compresses abdominal viscera, expiration.
Unilateral contraction - Trunk rotation (ipsilateral).
Nerve supply
Intercostal nerves (T7-T11), subcostal nerve (T12), iliohypogastric nerve (L1), ilioinguinal nerve (L1).
Blood supply
Lower posterior intercostal and subcostal arteries, superior and inferior epigastric arteries, superficial and deep circumflex arteries, posterior lumbar arteries.
Relevant research
A randomised trial found that in patients with an inguinal hernia, a transversus abdominis block is effective for pain control when the hernia is being repaired under general anaesthesia.
Theodoraki, K., Papacharalampous, P., Tsaroucha, A., Vezakis, A., & Argyra, E. (2019). The effect of transversus abdominis plane block on acute and chronic pain after inguinal hernia repair. A randomized controlled trial. International journal of surgery (London, England), 63, 63–70.
Tranversus abdominis exercises
None.
Sign UP
Sign up for your free trial now!
Get started with Rehab My Patient today and revolutionize your exercise prescription process for effective rehabilitation.
Start Your 14-Day Free Trial