Levator Palpebrae Superioris
Posted on 27th Jul 2020 / Published in: Face

General information
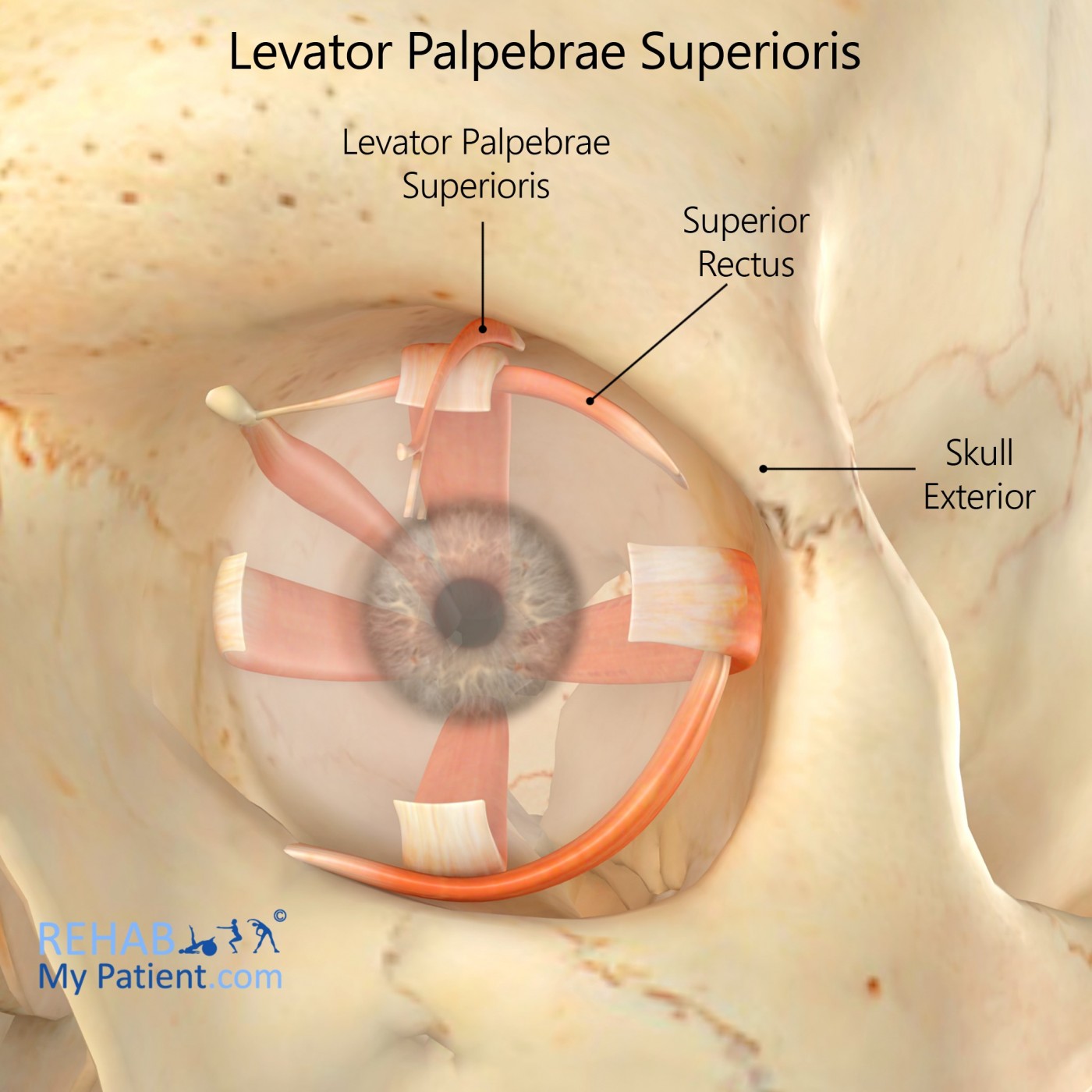
Levator palpebrae superioris is a facial muscle of the superior eyelid.
Literal meaning
The muscle that lifts the upper eyelid.
Interesting information
Levator palpebrae superioris is a skeletal muscle of the face that is responsible for elevating and retracting the superior (upper) eyelid.
Injury or dysfunction in levator palpebrae superioris or the oculomotor nerve (C3) which innervates it often results in ptosis, or marked drooping of the upper eyelid. However, ptosis may also be indicative of sympathetic nerve damage in nearby muscles including the superior tarsal muscle. For instance, a condition called Horner’s syndrome, or oculosympathetic palsy, generally presents with ptosis and results from damage to the sympathetic nerve system. It can be clinically distinguished from damage to the oculomotor nerve (C3) through examination of the pupil. Ptosis will be present in both cases but sympathetic nerve damage will result in a constricted pupil while a damaged oculomotor nerve will present with a dilated pupil (because of a lack of sphincter papillae innervation).
A blepharospasm is an uncontrolled and anomalous contraction or twitch of the eyelid muscles. The cause of these contractures is still unknown but possible triggers include stress, concussion, insufficient sleep, and a number of environmental irritants. Generally, the involuntary twitching resolves within a few hours or days of initial onset. But in rare instances the contractures can become chronic and even debilitating. In some cases, the contractures become so severe that a patient is unable to open their eyelids and is thus functionally blind. In those instances, botox injections, drug therapy, or surgical intervention may be required to recover proper eyelid function.
Origin
Lesser wing of the sphenoid bone.
Insertion
Tarsal plate and skin of the upper eyelid.
Function
Elevates the upper eyelid.
Nerve supply
Oculomotor nerve (C3).
Blood supply
Ophthalmic artery.
Relevant research
Using botulinum toxin (botox) to induce temporary ptosis (eyelid drooping) in levator palpebrae superioris is an effective method for increasing corneal protection during the healing process. Anterior injection should be implemented in order to prevent a decrease in superior rectus function.
Naik MN, Gangopadhyay N, Fernandes M, Murthy R, Honavar SG.(2008). “Anterior chemodenervation of levator palpebrae superioris with botulinum toxin type-A (Botox) to induce temporary ptosis for corneal protection”. Eye (Lond). 22(9):1132-6.
Although doctors, anatomists, and medical professionals have long been aware of the basic anatomical structure of levator palpebrae superioris, new surgical techniques and anatomical methods have allowed for a more comprehensive understanding of the muscle and its surrounding structures.
Ng SK, Chan W, Marcet MM, Kakizaki H, Selva D. (2013). “Levator palpebrae superioris: an anatomical update”. Orbit. 32(1):76-84.
Levator palpebrae superioris exercises
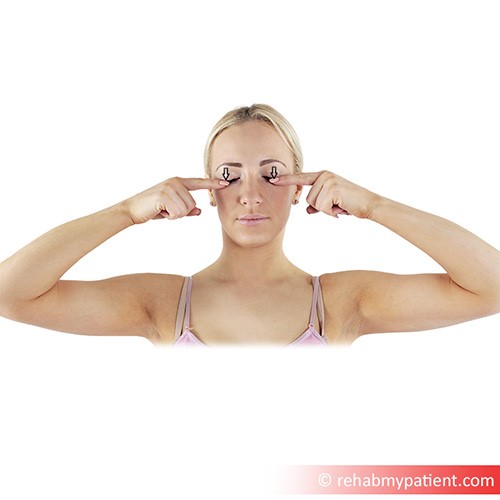
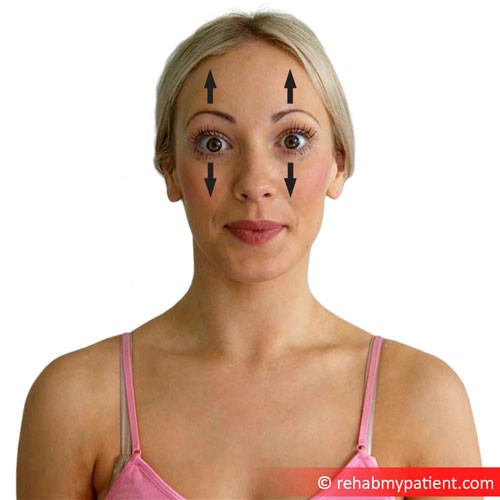


To strengthen levator palpebrae superioris and to relieve bothersome eyelid twitching, you should perform targeted eyelid exercises daily. First, close your eyelids as tightly as you can and hold that position for ten whole seconds. Then open your eyes as wide as possible and hold them at that extreme for ten seconds. Continue to alternate between squeezing your eyes shut and opening them up wide. Complete a total of ten sets daily.
Sign UP
Sign up for your free trial now!
Get started with Rehab My Patient today and revolutionize your exercise prescription process for effective rehabilitation.
Start Your 14-Day Free Trial