Intercostals
Posted on 24th Jul 2020 / Published in: Ribs

General information
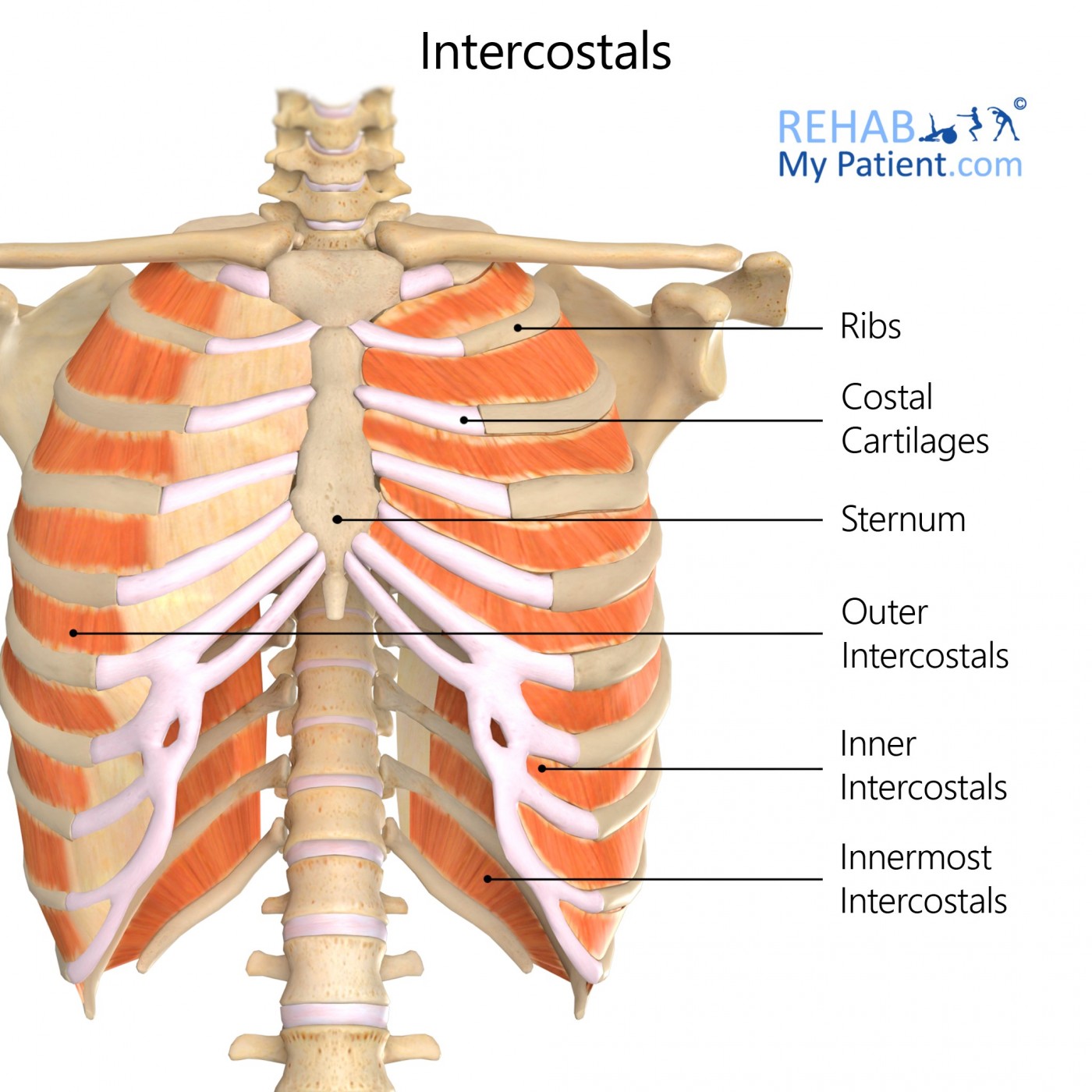
The intercostal muscles are made up of the intrinsic muscles of the rib cage which are situated in the 11 intercostal spaces. There are three groups within the intercostals, situated superficially down to deep:
- External intercostal muscles
- Internal intercostal muscles
- Innermost intercostal muscles
Literal meaning
External intercostal muscles - the outward muscle between the ribs.
Internal intercostal muscles - the within (middle) muscle between the ribs.
Innermost intercostal muscles - the inmost muscle between the ribs.
Interesting information
These muscles are accessory respiratory muscles that aid in forced breathing. The external intercostals assist in forced inspiration, and the internal and innermost intercostals help with forced expiration.
Any deficits in the intercostal muscles may lead to chest wall movement during changes in thoracic pressure, this is because there is inadequate tension of the intercostal spaces. This can then cause respiratory insufficiency.
Origin
External, internal, and innermost intercostal muscles - Inferior border of superior rib.
Insertion
External, internal, and innermost intercostal muscles - Superior border of adjacent inferior rib.
Function
Mechanical support to the thoracic cage, accessory respiratory muscles.
Nerve supply
External, internal, and innermost intercostal muscles - Intercostal nerves (T1 through T11).
Blood supply
External intercostal muscles - anterior and posterior intercostal arteries.
Internal intercostal muscles - the anterior and posterior intercostal arteries, as well as from the costocervical trunk, internal thoracic and musculophrenic arteries.
Innermost intercostal muscles - the anterior and posterior intercostal arteries, costocervical trunk, internal thoracic and musculophrenic arteries.
Relevant research
None
Intercostal exercises
None
Sign UP
Sign up for your free trial now!
Get started with Rehab My Patient today and revolutionize your exercise prescription process for effective rehabilitation.
Start Your 14-Day Free Trial