
General information
The Extensor digitorum brevis – occasionally referred to as EDB – is a small muscle on the dorsum of the foot that is involved in the extension of digits two-through-four.
Literal meaning
The literal meaning of extensor digitorum brevis is “short toe extender”, perfectly describing its purpose.
Interesting information
The extensor digitorum brevis can act as a trigger point for foot pain, although this may overlap with pain from the tibialis anterior and peroneus terius. Pain and inflammation at these trigger points can also lead to cramping during the night and a condition known as hammer toe.
Pain in the extensor digitorum brevis is often linked to poor footwear choices or frequent walking and running on uneven surfaces that place a disproportionate workload on the muscles of the foot. Excessive or poorly-executed exercises such as weighted calf raises can also trigger pain and inflammation in the extensor digitorum brevis.
Another particularly common culprit of foot pain is the infamous high-heeled shoe, with extra strain being placed on the dorsal muscles as the foot slides into the shoe.
The extensor digitorum brevis can easily be located by dorsiflexing the foot (pulling the toes up towards the knee) and observing the muscular contraction on the top-outer portion of the foot.
Generally speaking, the muscles of the foot are close to the surface of the skin so massage and rehabilitation do not usually require a significant amount of force. Investing in a pair of comfortable shoes that provide adequate support is the ideal long-term strategy, and pain can be treated by simply using the hands to massage the affected area.
Origin
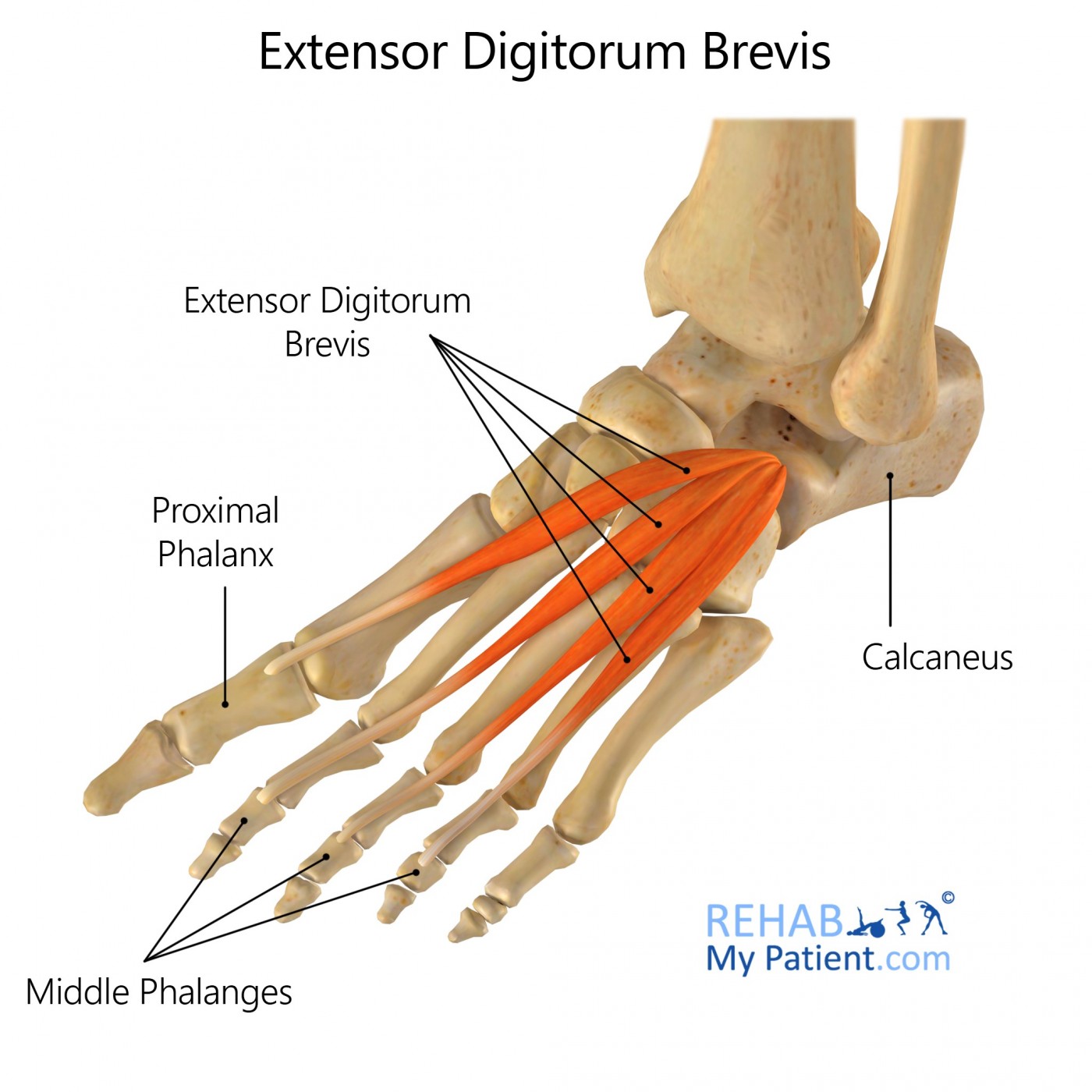
Upper and lateral surface of calcaneus, in front of groove for peroneus brevis, from interosseous talocalcaneal ligament, stem of inferior extensor retinaculum.
Insertion
Four tendons extending into the proximal phalanx of the big toe and long extensor tendons to toes 2, 3 and 4.
Function
The function of the extensor digitorum brevis is to extend or straighten the middle three toes when the foot is fully dorsiflexed.
Nerve supply
Deep peroneal nerve.
Blood supply
Dorsalis pedis artery.
Relevant research
A 1987 study demonstrated the efficacy of the extensor digitorum brevis muscle flap in covering defects of the distal tibia and malleoli as an island muscle flap.
Hing DN, Buncke HJ, Alpert BS. Applications of the extensor digitorum brevis muscle for soft tissue coverage. Ann Plast Surg. 1987 Dec;19(6):530-7,
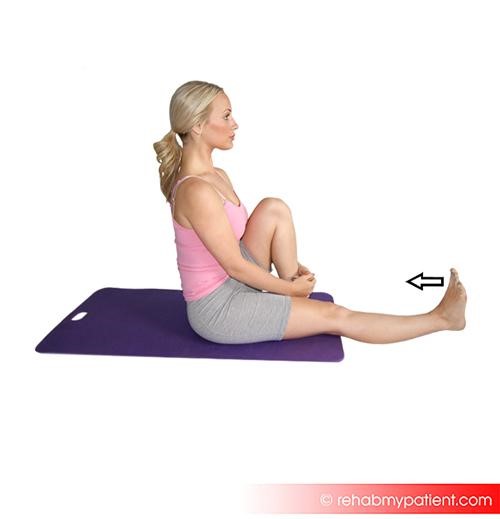
Extensor Digitorum Brevis exercises
A trigger point in the foot is essentially a bundle of knotted muscle fibers. Even if the knot does not hurt it may refer pain elsewhere, making it difficult to pinpoint the exact origin of the pain. It is, therefore, important to locate and treat the right spot.
Movements involving dorsiflexion of the foot in addition to targeted massage will provide some pain relief in the extensor digitorum brevis.
The following dorsiflexion protocol may be effective in strengthening the muscles of the foot and ankle and providing some degree of fascial release of the extensor digitorum brevis. To do the exercise, simply pull your ankle and toes towards you. Hold this position for 10 seconds, and repeat 2-3 times, alternating between each foot.

Reference
Kelikian, Sarrafian (2011), Sarrafian's Anatomy of the Foot and Ankle: Descriptive, Topographical, Functional,Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
Sign UP
Sign up for your free trial now!
Get started with Rehab My Patient today and revolutionize your exercise prescription process for effective rehabilitation.
Start Your 14-Day Free Trial