Extensor Digitorum
Posted on 23rd Jul 2020 / Published in: Hand/Fingers/Thumb , Wrist

General information
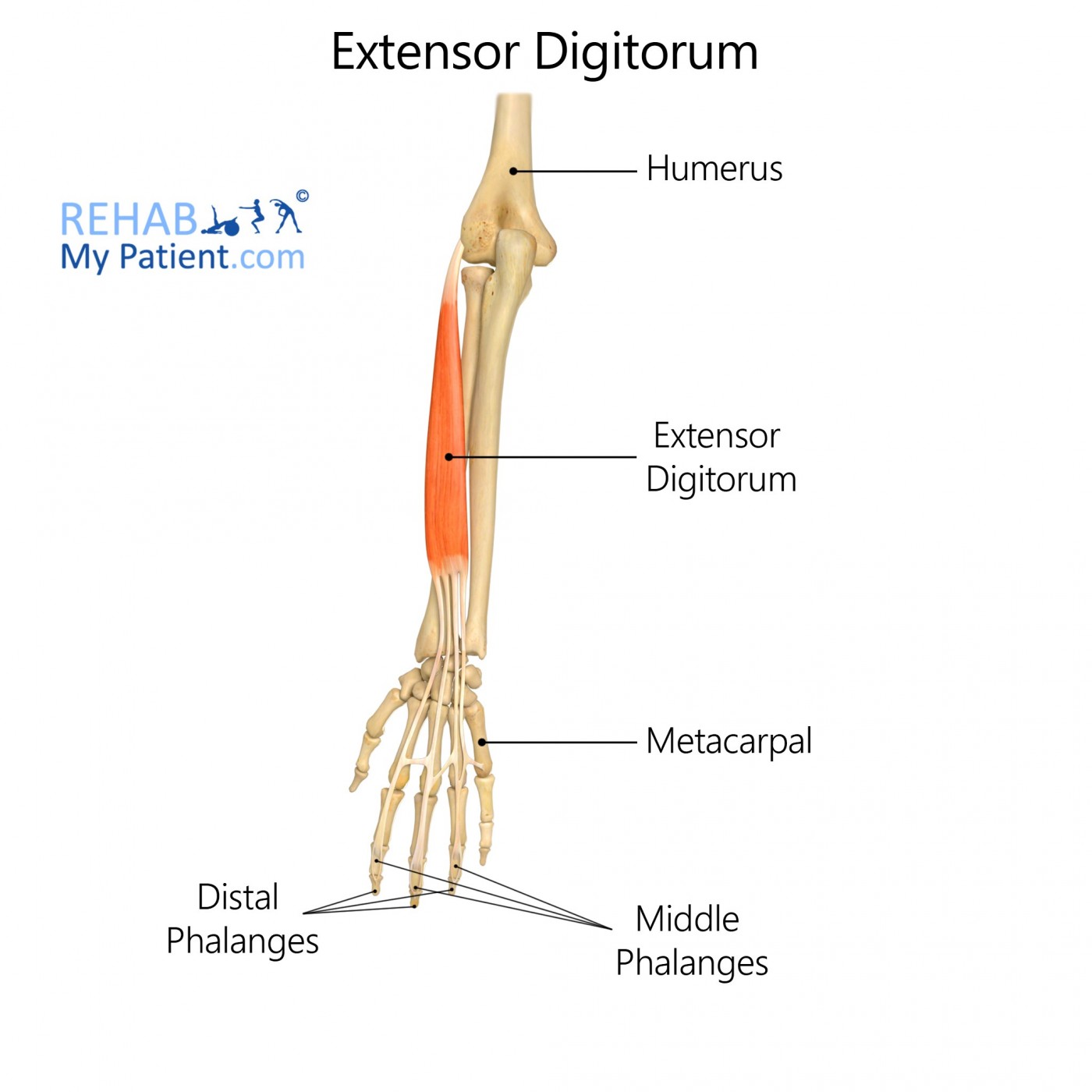
Extensor digitorum is a muscle of the posterior forearm and is sometimes referred to as extensor digitorum communis.
Literal meaning
The muscle that extends the fingers.
Interesting information
Due to the location and function of extensor digitorum, it is essential in many daily activities that require extension of the wrist and hand including waving. Therefore, any injury to the muscle can be debilitating and take significant time to heal.
A common type of injury that can affect extensor digitorum is tennis elbow. This injury is typically caused by overuse of the extensor muscles which attach at the elbow. Symptoms of tennis elbow include marked weakness in the wrist and hand along with pain localized to the outside of the elbow. The treatment usually involves resting the affected extensor muscles along with ice and compression.
As extensor digitorum extends the fingers, it also tends to separate them.
Origin
The lateral epicondyle of the humerus (via the common extensor tendon).
Insertion
The posterior surface of the phalanges of the 2nd, 3rd, 4th, and 5th fingers (via the extensor expansion).
Function
Extension of the wrist, hand, and fingers.
Nerve supply
The radial nerve (C7 and C8).
Blood supply
Posterior interosseous artery.
Relevant research
Researchers hypothesized that extensor digitorum parts leading to the fingers have separate functionality and activity which would be recordable through surface electromyography (EMG) electrodes. The resulting measurements derived from this study could expand on current understanding and clinical application of EMG analysis and finger muscle electro-stimulation.
J.N.A.L. Leijnse, N. H. Campbell-Kyureghyan, D. Spektor, P. M. Quesada (2008). “Assessment of Individual Finger Muscle Activity in the Extensor Digitorum Communis by Surface EMG”. J Neurophysiol. 100(6):3225-35.
This study examined synchronization activity in pairs of motor units in the right extensor digitorum communis muscle. Muscle pair contractile properties were recorded using electrodes and characterized according to their properties. The ability of subjects to voluntarily control muscle synchronization was measured and results suggested supraspinal centres can indeed control some motorneuron synchronization during voluntary activation of extensor digitorum communis.
Schmied A, Ivarsson C, Fetz EE (1993). “Short-term synchronization of motor units in human extensor digitorum communis muscle: relation to contractile properties and voluntary control”. Exp Brain Res. 97(1):159-72.
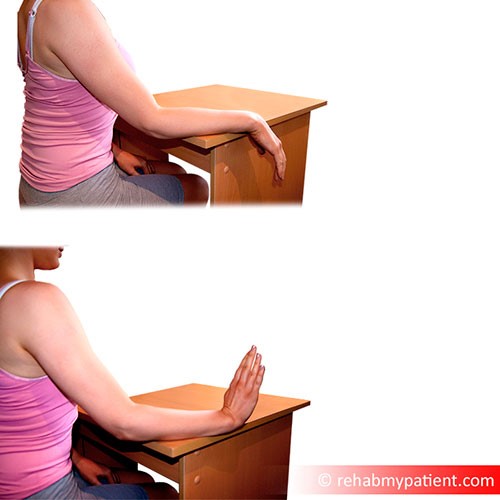
Forearm extensor exercises

Hold your arm in front of you, with your thumb facing up. Deviate your hand to one side, and then the other. This exercise will help improve the mobility of your wrist. Repeat ten times.
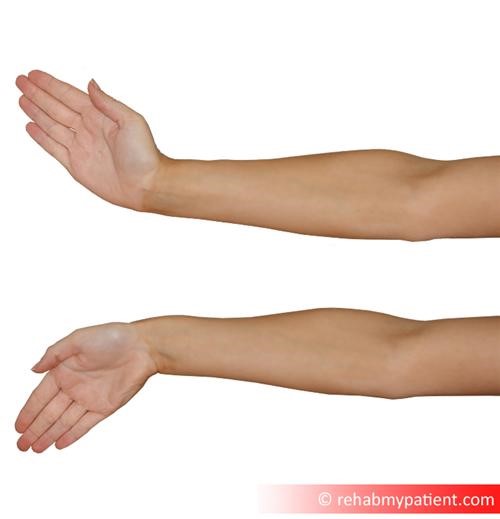
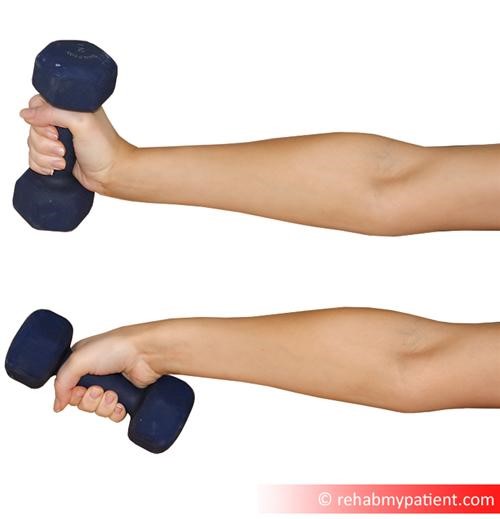
To increase the impact of this exercise and to add an element of strength training, repeat the same movement while holding a small dumbbell in your hand.

Sign UP
Sign up for your free trial now!
Get started with Rehab My Patient today and revolutionize your exercise prescription process for effective rehabilitation.
Start Your 14-Day Free Trial